When it comes to emergencies, many wonder, “Can a jump starter charge a battery?” The answer is no—it just provides a quick power boost. Jump starters deliver 300 to 2000 amps, enough to start the engine but not recharge the battery. Find affordable options in the 6 Best Budget Jump Starter in 2024.
If your battery is deeply drained, you’ll need more than just a jump starter. After starting, driving for at least 15-20 minutes helps the alternator add some charge, but it may not fully restore a dead battery.
Quick Look
A jump starter cannot charge a battery. It only provides a temporary power boost to start the engine. For a full recharge, you need a battery charger, which supplies a continuous flow of electricity to restore the battery’s energy.
Can a jump starter fully charge a dead battery?
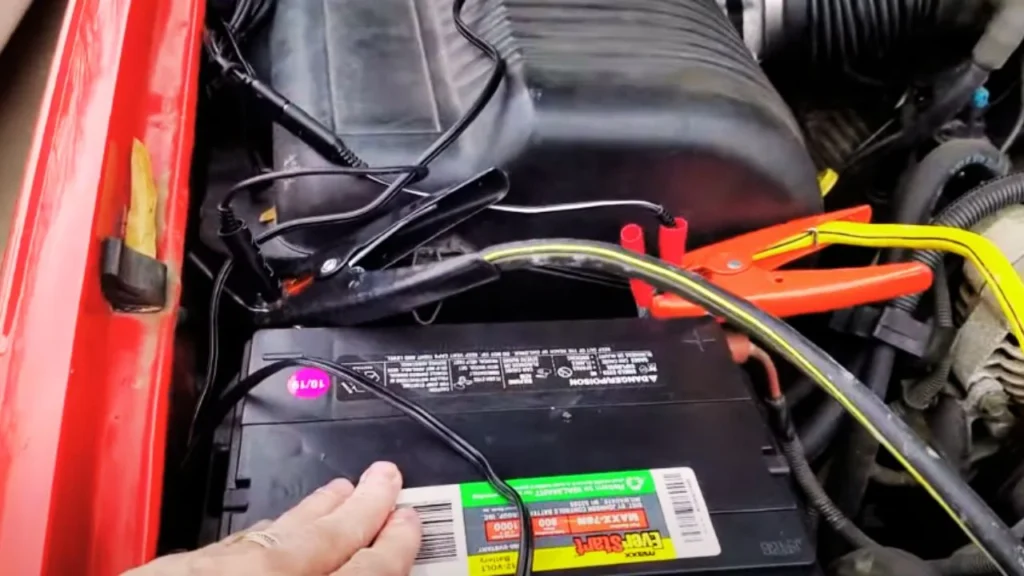

No, a jump starter cannot fully charge a dead battery. It’s designed to provide a quick power boost to start the engine, not to replenish the battery’s energy. For a complete recharge, use a battery charger, which can take several hours to fully restore the battery.
Can a Jump Starter Charge a Battery?

So, can a jump starter actually charge your car battery? The short answer is no. A jump starter is designed to provide a quick burst of power—around 400 to 2,000 amps—just enough to start your engine. It doesn’t replenish the battery’s energy.
When you use a jump starter, it helps get your car going, but that’s where its job ends. After the jump, it’s the alternator that kicks in to recharge the battery. It can take around 10-15 minutes of driving to give your battery a decent boost, but not a full charge.
A car battery typically needs a charge of 12.6 volts or higher to operate effectively. After a jump-start, your alternator generates around 14 volts to slowly replenish the battery. If your battery is heavily drained, though, it could take hours—or even a dedicated battery charger—to fully recharge it.
How a Jump Starter Works

Let me break down how a jump starter actually works. When your car battery fails, a jump starter provides a short burst of high-amperage power. We’re talking about 200 to 2,000 amps, depending on the model, just enough to crank up the engine.
The device connects directly to your battery’s terminals, delivering that power surge in a few seconds. It doesn’t refill your battery; instead, it helps spin the starter motor to get the engine running. Once the engine’s on, the alternator kicks in and starts charging the battery at around 13.5 to 14.5 volts.
Jump starters come in handy because they’re portable and easy to use. You might get around five to 20 jump-starts from a fully charged unit, depending on the battery capacity. But remember, it’s not meant for deep charging; it’s a quick-fix solution to get you back on. Master the skills with the How to Jump Start a Car by Yourself – Complete Guide.
Purpose of a Jump Starter
You might think that a jump starter and a battery charger do the same thing, but they’re actually quite different. A jump starter is like a quick fix—it delivers a powerful burst of current.
How a Battery Charger Works

A battery charger is more like a long-term solution. It sends a low-amperage current, usually between 1 and 10 amps, to gradually recharge the battery. Depending on the charger and the battery’s condition, this process can take anywhere from 4 to 24 hours.
When to Use Each Tool
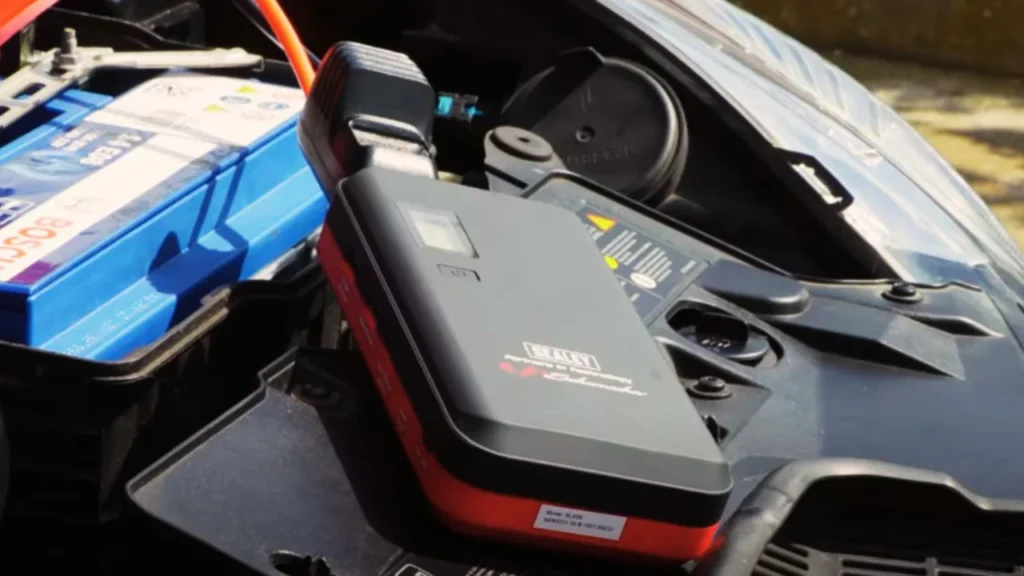

If you’re in a hurry and need to get back on the road, a jump starter will do the trick. However, it’s not going to bring your battery back to full strength. That’s where the charger comes in—it fills up the battery slowly, helping maintain a steady power level that can last much longer. Understand the process with the Can You Jump Start a Car Without a Battery? Guide 2024.
Situations Where a Jump Starter May Not Work
Let me tell you, using a jump starter isn’t always a guaranteed fix. There are times when that little boost of power just won’t cut it.
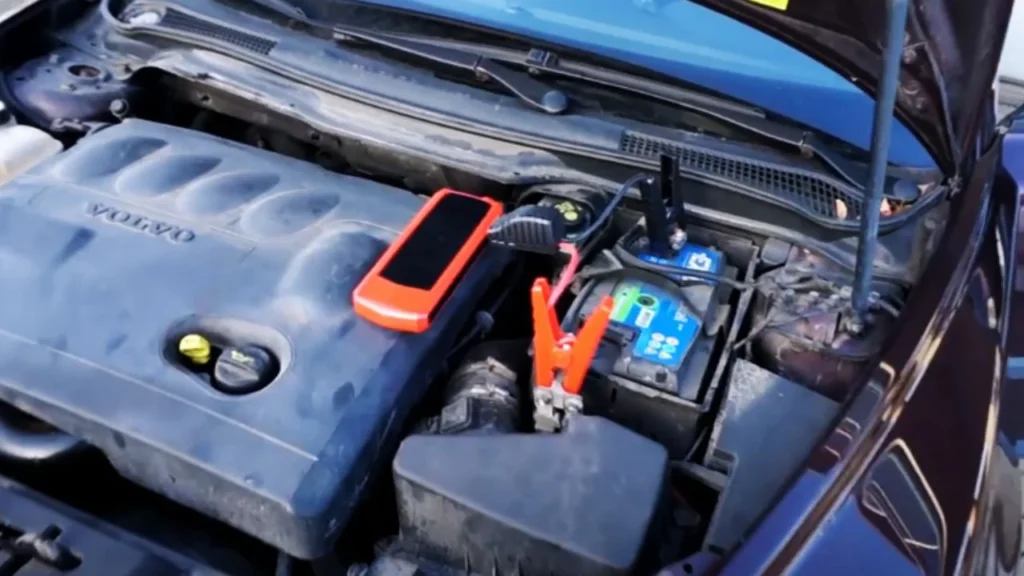

Low Voltage Levels
Let’s start with the voltage. If your battery’s voltage has dropped below 12 volts, a jump starter might struggle to get it going. Healthy batteries usually rest around 12.6 volts, and anything much lower indicates a deep discharge.
Age of the Battery
Then there’s the age factor. If your battery is over five years old, it may be nearing the end of its lifespan. Most car batteries last about 3-5 years under normal conditions. Beyond that, they lose their ability to hold a charge, even with frequent jump-starting.
Problems with the Alternator
Now, let’s talk about the alternator. Its job is to recharge the battery while the car is running, but if it’s malfunctioning, the battery won’t receive enough charge. A properly functioning alternator should generate around 14 volts while the engine is running. If it produces less, the battery will continue draining.
Extreme Weather Conditions
Temperature plays a role too. Batteries can lose 20% of their capacity in cold weather (below 32°F or 0°C) and up to 50% when temperatures drop to -22°F (-30°C). If you’re dealing with extreme cold, a jump starter might not provide enough power to crank the engine.
Internal Battery Damage
Internal damage is another issue to consider. If a battery has corroded terminals or internal short circuits, even a fully charged jump starter may not help. Corrosion around the terminals can increase electrical resistance, making it difficult for a jump starter to deliver power effectively.
Electrical Drain from Accessories
Finally, electrical drain from car accessories can be a problem. Leaving the headlights or interior lights on can drain the battery quickly. If you’re jump-starting the car and these accessories are still drawing power, it might take more than one attempt. Discover the Top 6 Best Car Jump Starter with an AC Outlet 2024 Picks for versatile power solutions.
Limitations of a Jump Starter
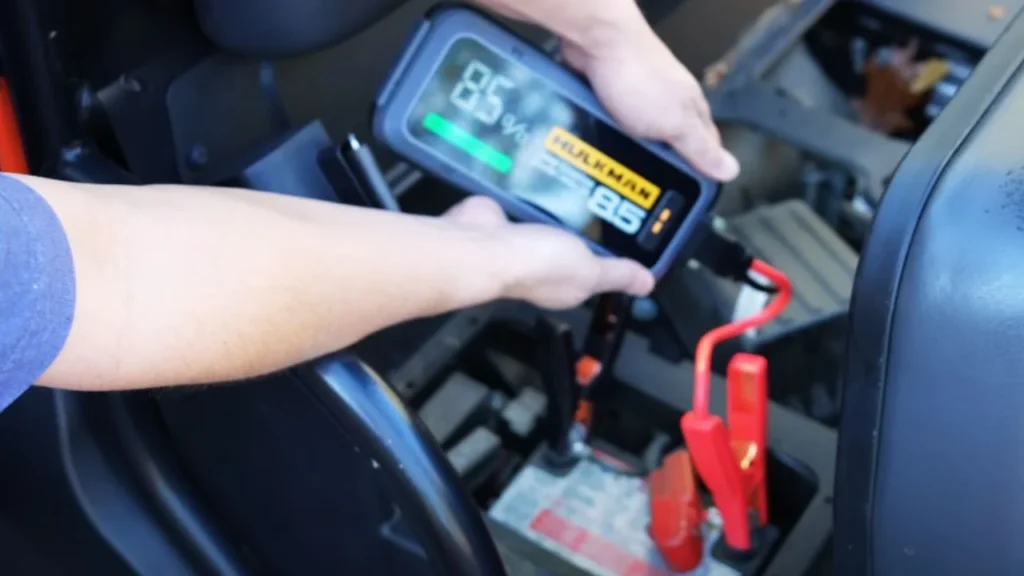

You might think a jump starter can do the trick, but trust me, it’s not designed for fully recharging a battery. When a car battery is completely drained, it typically takes a battery charger between 10 to 24 hours to fully recharge it.
Amps and Charging Rates Matter
Jump starters only provide a quick jolt, usually around 1,000 to 2,000 amps, to get the engine running. In contrast, battery chargers work at much lower amperage, usually 2 to 10 amps, to recharge the battery gradually. This slow charge is essential for maintaining the battery’s health and longevity.
Regular Charging Extends Battery Life
For a healthy car battery, aim to recharge it fully once every three months, especially if it’s not in regular use. Regular charging helps maintain the voltage at around 12.6 volts, which is ideal. If you keep using a jump starter alone, you’ll risk reducing the battery’s lifespan by up to 50%.
Safety Tips for Using a Jump Starter
Using a jump starter isn’t complicated, but safety should always come first. Following these tips can help you avoid common mistakes and keep your car and yourself protected. Let’s look at some easy ways to jump-start your car safely.
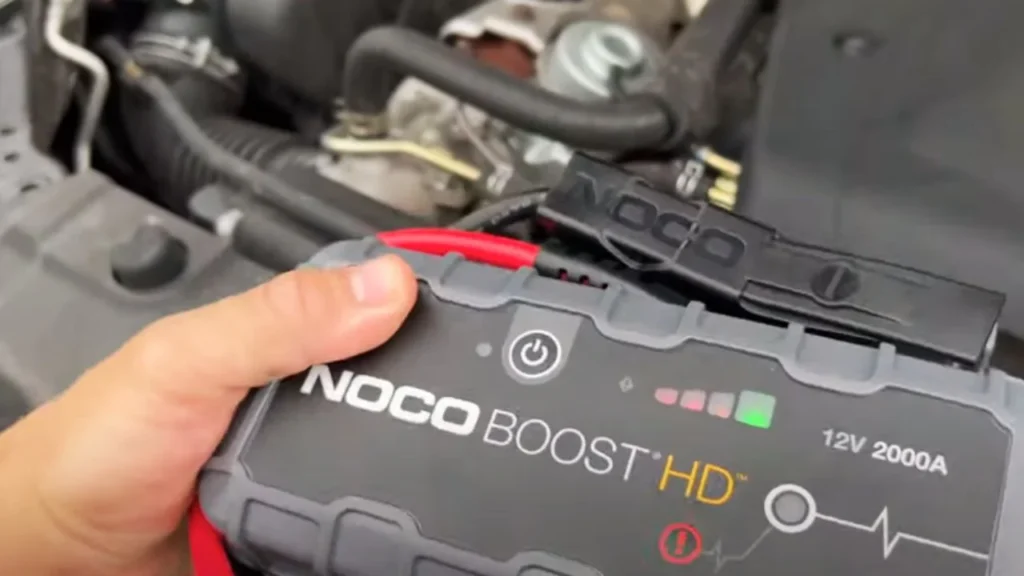

Proper Clamp Connections are Essential
When it comes to using a jump starter, safety is crucial. Did you know that over 30% of car battery-related accidents happen due to improper handling? It’s easy to avoid these risks with a few simple precautions.
Connect the Clamps in the Right Order
Always connect the positive clamp (red) to the positive terminal on your battery and the negative clamp (black) to an unpainted metal surface. This reduces the chance of sparking, which can be dangerous. Over 50% of jump starter issues arise from incorrect connections.
Ensure Your Jump Starter is Fully Charged
Make sure the jump starter is fully charged before you use it. A jump starter at 20% charge or less won’t be able to deliver enough power to start your car. Keep an eye on the charge level and top it off every three months to maintain peak performance.
Position the Jump Starter Safely
Position the jump starter on a stable surface away from moving engine parts. The last thing you want is for it to slip and fall into the engine while starting your car. Trust me, it happens more often than you’d think—around 10% of the time, according to user reports.
Disconnect the Cables Correctly
After successfully jump-starting the car, disconnect the cables in the reverse order: first the black, then the red. This reduces the risk of accidental short-circuits, which cause nearly 25% of battery-related damage. Learn about carrying a jump starter on a plane with the Can I Take a Jump Starter on a Plane? 2024 Guidelines.
Recharge the Jump Starter After Use
Lastly, don’t forget to recharge the jump starter itself. If you’ve used it a couple of times, make sure to plug it in and let it charge fully. Keeping it charged can add up to 30% more lifespan to the device.
Final Words
Can a jump starter charge a battery? Not exactly—it’s meant for quick boosts, not long-term charging. While it can get you back on the road in seconds, remember, it doesn’t replenish your battery.
After a jump, let the engine run for at least 15 minutes, giving the alternator time to do its job. For a complete recharge, consider a battery charger, which can take 10-24 hours to fully charge a depleted battery.