So, you’re here to learn how to jump start a diesel truck, right? It’s different from a regular vehicle since diesel engines typically need two 12V batteries to start. This extra power is necessary because these engines operate with compression ratios as high as 20:1. Looking for the best jump starter for electric vehicles? Check out our detailed reviews on the best jump starters for EVs.
Diesel trucks can take 10 minutes or more to jump-start, so patience helps. If your batteries die, it’s good to know this isn’t rare—especially when one battery drains faster. But once you understand the steps, you’ll be back on the road quickly and safely!
Quick Look
To jump-start a diesel truck, connect the positive jumper cable to the positive terminals on both the dead and donor batteries. Then, attach the negative cable to the donor battery and ground the other end on the dead truck’s engine block. Start the donor vehicle, let it run for a few minutes, and then attempt to start the truck.
Can I jump start a diesel truck using a gasoline vehicle?

Yes, you can jump-start a diesel truck with a gasoline vehicle, but only if the donor vehicle has a battery capable of providing sufficient cranking amps.
Diesel engines require more power to start due to their higher compression ratios, and gasoline vehicles might not always meet these power demands. Use heavy-duty jumper cables to ensure proper current flow.
Remember that repeated attempts may drain the donor battery if it’s underpowered. It’s essential to follow the correct connection sequence to avoid damaging electrical components on either vehicle. Find the top-rated options by exploring our recommendations for the best portable jump starters on the market.
Tools and Equipment Needed

Before getting started, having the right tools makes jump-starting your diesel truck faster and safer. Diesel engines require more power to start than gasoline ones, so being well-prepared ensures you’re not left stranded. Whether you’re using another vehicle or a portable jump starter, here are the essentials you need.
- Heavy-duty jumper cables: Look for 4 or 6-gauge cables, ideally 12 to 20 feet long, to reach both batteries comfortably.
- Donor vehicle or jump starter: Ensure it has the capacity to provide 12 volts to match the truck’s system.
- Gloves and safety glasses: Essential to protect yourself from sparks and potential acid exposure.
- Multimeter (optional): Use this to confirm the battery’s voltage; a good reading is about 12.6 volts.
- Open, ventilated space: Reduces the risk of gas buildup from the batteries, making the process safer.
Step-by-Step Guide: How to Jump Start a Diesel Truck
Let’s walk through the steps to jump-start your diesel truck so you can hit the road again. Diesel trucks can be tricky because they often come with two batteries, meaning precision and patience are key. Below, I’ll break down the process into easy-to-follow steps so you can get the job done right the first time.
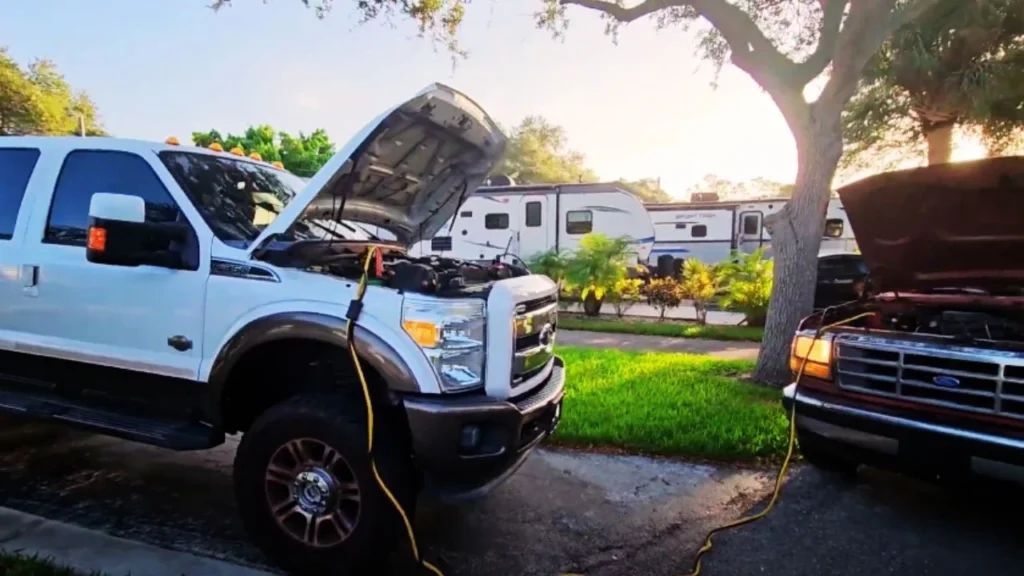
Step 1: Position the Vehicles

Park the vehicles close to each other, ideally within 3 feet, but ensure they’re not touching. Make sure both trucks are in park or neutral with parking brakes engaged, and switch off all electronics to avoid electrical issues during the process.
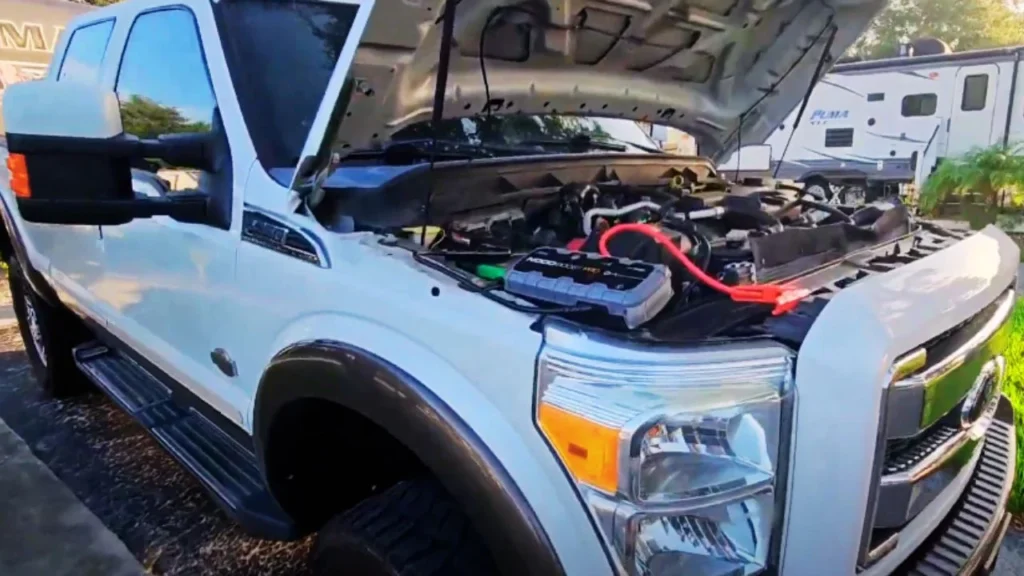
Step 2: Connect the Positive Cables
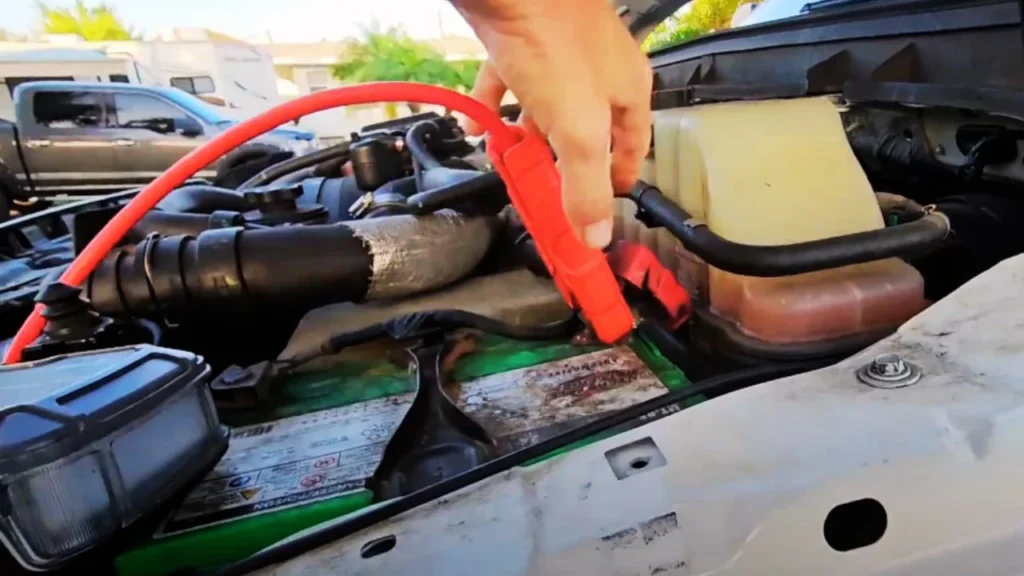

Attach the positive (red) clamp to the positive terminal on the dead truck’s battery. Then, connect the other end to the positive terminal of the donor vehicle’s battery. Always connect positive terminals first to minimize the risk of sparks.
Step 3: Connect the Negative Cables
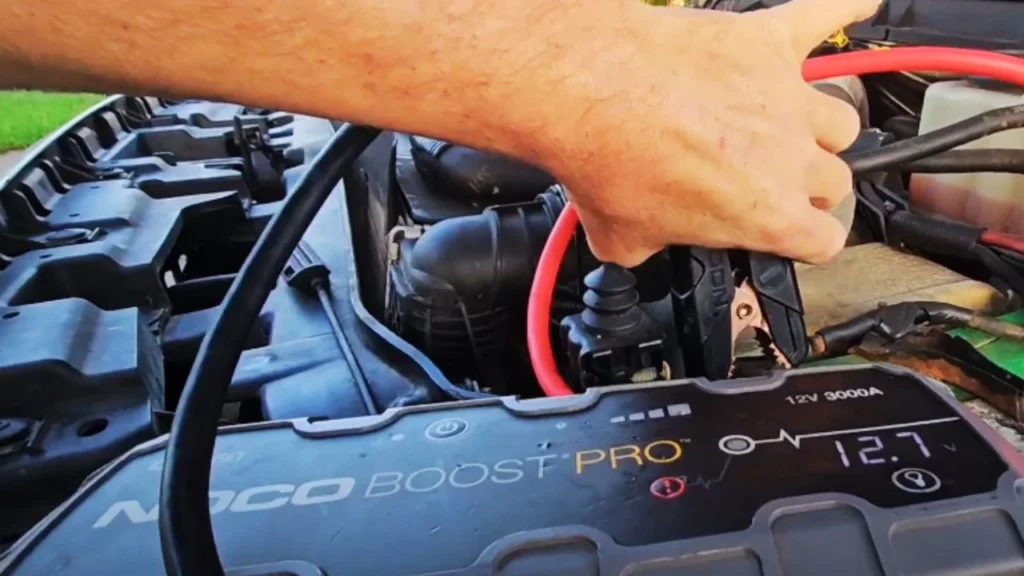

Now, clamp the negative (black) cable to the donor vehicle’s negative terminal. For the dead truck, ground the other black clamp to a metal surface—like the engine block or chassis—for safety instead of the battery terminal directly.
Step 4: Start the Donor Vehicle
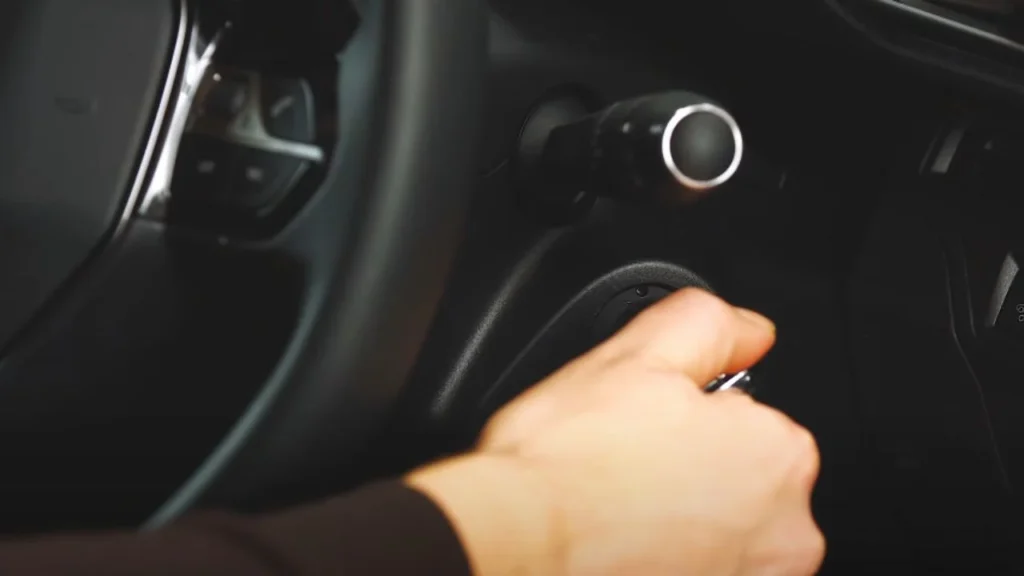

Turn on the donor vehicle and let it idle for 5 minutes, revving it gently to 1,500 RPM to help charge the dead batteries. Keep it running to ensure a consistent energy flow to the truck that needs the jump.
Step 5: Start the Diesel Truck
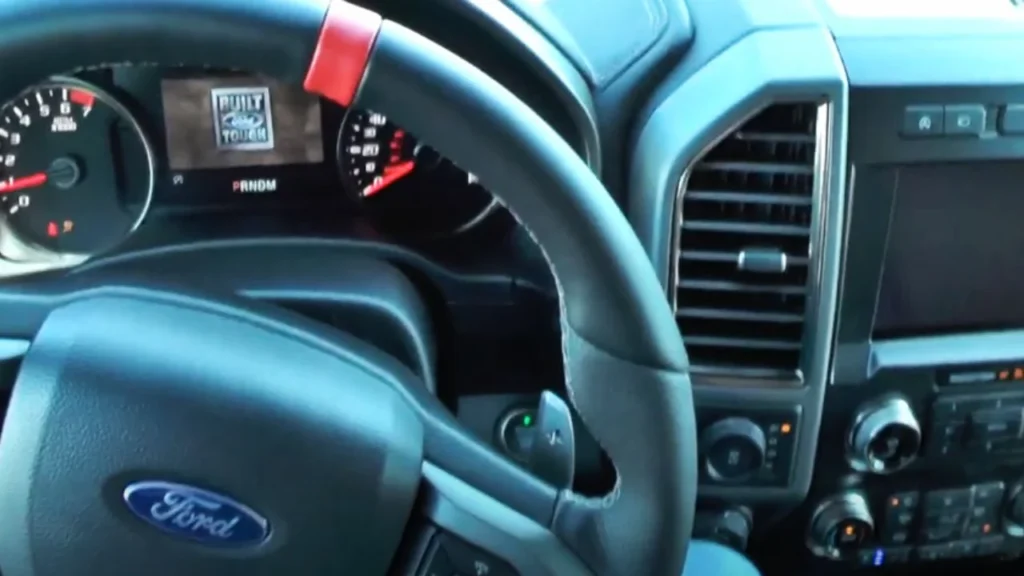

Try starting the diesel truck. If it doesn’t start immediately, give it another 2-3 minutes to build enough charge. Once the engine roars to life, keep both vehicles running for 10-15 minutes to recharge the dead batteries further.
Step 6: Disconnect the Cables
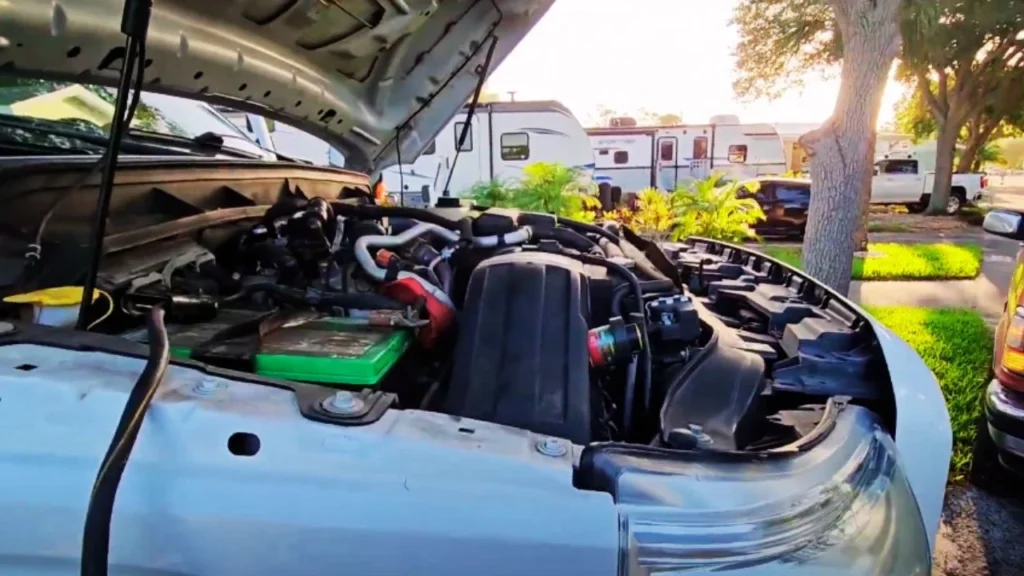

Remove the cables in reverse order: first the black cable from the grounded surface, then the negative terminal of the donor vehicle. Finally, remove both positive clamps. Be cautious while disconnecting, making sure the clamps don’t touch.
Step 7: Take the Truck for a Drive

To recharge the batteries fully, drive the truck for 20-30 minutes without shutting it off. This ensures the alternator can top off the batteries, reducing the chance of another dead battery scenario soon after. Using a portable jump starter? Make sure you know the right steps by reading how to charge a portable jump starter efficiently.
Post-Jumpstart Checks and Next Steps
After jump-starting the truck, I always ensure to drive for at least 20 to 30 minutes. This gives the alternator enough time to fully recharge the batteries. If I cut the drive short, there’s a risk of only achieving about 50% battery capacity, which might not be enough to avoid another stall.
I also like to test the battery with a multimeter to confirm it’s healthy. A good battery should show around 12.6 volts when idle. If it dips below 12.4 volts after the drive, it could mean either the battery is weak, or the alternator needs attention.
Safety Guide for Jump-Starting a Diesel Truck
Jump-starting a diesel truck is simple but must be done with care to avoid injury or damage. Following safety precautions ensures the process goes smoothly, preventing sparks, battery explosions, or electrical shorts. Here’s everything you need to know to jump-start your truck safely and confidently.
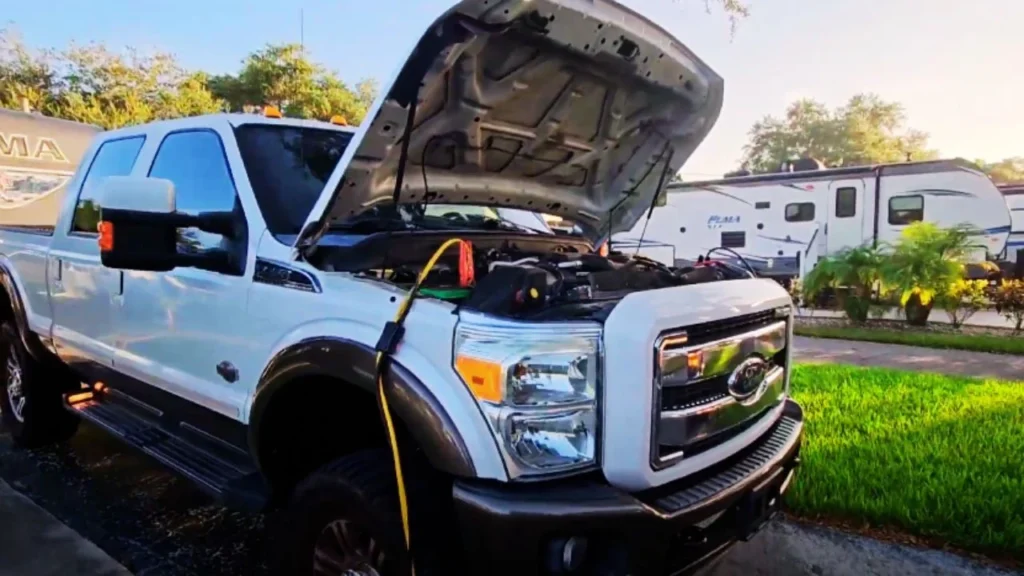

Protective Gear
Wear safety glasses and gloves to shield yourself from sparks or battery acid. Batteries can release hydrogen gas, which is flammable, so wearing proper gear reduces risk. Avoid wearing loose clothing to prevent entanglement with engine components.
Use Well-Maintained Equipment
Ensure jumper cables are heavy-duty (4-gauge or 6-gauge) and free from damage. Damaged cables can cause electrical issues or shorts. Before connecting, verify the batteries are compatible to ensure smooth power transfer.
Choose a Safe Location
Work outdoors or in a ventilated space to avoid hydrogen gas buildup. Keep vehicles 2 feet apart but close enough to connect the cables comfortably. Avoid performing the jump-start in wet conditions to minimize electrical risks.
Correct Cable Connection Sequence
Always connect the positive cable first to prevent dangerous sparks. Use a bare metal surface on the dead vehicle for grounding the negative cable. Follow the correct removal order: negative cables first, then positive, to protect electrical systems.
Avoid Flames and Smoking
Never smoke or bring open flames near the batteries. Sparks or flames can ignite hydrogen gas, causing fire or explosions. If sparks occur during connection, stop immediately and recheck the setup.
Post-Jump Checklist
Let the truck run for 20-30 minutes to recharge the batteries fully. Inspect lights, radios, and other electrical components to ensure no damage occurred. If the truck still fails to start, consult a professional mechanic.
Final Words
So, that’s how I handled the process of how to jump start a diesel truck. Honestly, it’s not as intimidating as it seems—just a little patience and the right tools can get you back on the road. In under 20 minutes, you can revive your truck and avoid a costly towing fee.
Remember, most diesel trucks need two batteries to power up those high-compression engines. If you stay safe and follow the steps, you’ll drive worry-free for another 30 minutes to recharge the batteries fully. Always be prepared for the unexpected!
FAQ’s
What if the truck doesn’t start after several attempts?
If your diesel truck doesn’t start after several attempts, begin by inspecting the battery connections for corrosion or looseness, as poor contact can block power transfer. Use a wire brush to clean terminals if necessary.
Additionally, the problem could indicate deeper issues such as a faulty alternator, which may not be recharging the battery, or a completely dead battery that cannot hold a charge.
If tightening connections and further charging attempts don’t work, it may be time to seek professional help to diagnose underlying electrical or mechanical problems. If your jump starter isn’t working as expected, follow our guide on how to reset a jump starter to get it back in action.
What are the signs of a bad battery versus a faulty alternator after a jump-start attempt?
A bad battery typically shows signs like dim headlights, slow cranking, or a clicking sound when you try to start the truck, even after a jump-start. If the truck stalls again soon after starting, it may indicate the battery isn’t holding a charge.
On the other hand, a faulty alternator may allow the engine to start with a jump but will fail to recharge the battery, causing the truck to lose power quickly.
Other signs of a bad alternator include flickering dashboard lights, electrical malfunctions, and whining noise from the engine area
How long should you run the truck after jump-starting to fully recharge the batteries?
After jump-starting a diesel truck, you should let it run for at least 20 to 30 minutes to allow the alternator to recharge the batteries. This gives the alternator enough time to replenish the energy lost during the failed start attempt.